Quick Definition
Thermal resistance (R-value) indicates a material’s resistance to conductive heat flow. The higher the R-value, the greater the insulating effectiveness is of that material. The R-value is the inverse of the U-value that measures how readily a substance conducts heat. (Yudelson)
Wall, roof, and floor assemblies are required by code to have a minimum R-value. A higher R-Value means your home is better prepared to stay cool in the summer and warm in the winter.
In Depth
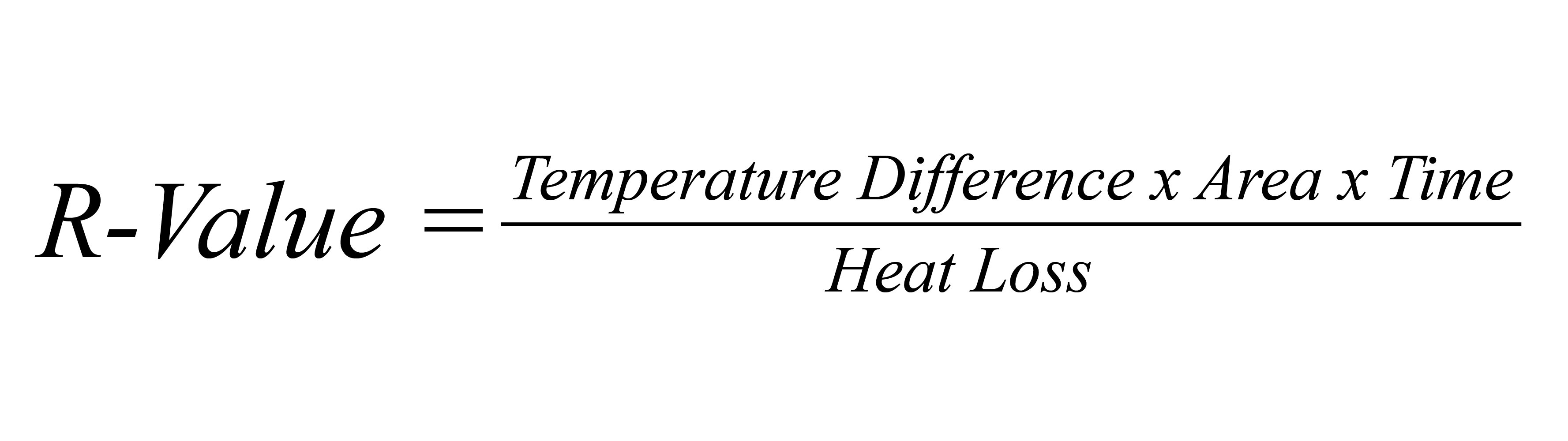
R-Values are calculated using the following equation:
R-Value = temperature difference x area x time / heat loss
Material tables show R-Values for a wide range of construction materials. Most people are concerned with the R-Values of wall types and insulation.
Insulation R-Values
The R-Value for most wall / roof / floor assemblies depends on the R-Values of the insulation components used in a home. The R-value of insulation varies based on the type of insulation used, its thickness and its density. Here are the typical R-values for some common insulation types, based on 1” of insulation:
- Fiberglass Batts: R-3.1
- Fiberglass Blown (attic): R-2.2-4.3
- Fiberglass Blown (wall): R-3.7-4.3
- Rock Wool Batt: R-3.1-4.0
- Rock Wool Blown (attic): R-3.1-4.0
- Rock Wool Blown (wall): R-3.1-4.0
- Cellulose Blown (attic): R-3.6-3.7
- Cellulose Blown (wall): R-3.8-3.9
- Closed cell polyurethane spray foam: R-6.8
- Extruded or expanded polystyrene: R-4.0-5.0
An expanded list of insulation values can be seen at Colorado Energy and Wikipedia.
Two additional great resources for more information:
Energy Star Recommended Levels of Insulation
Department of Energy on Insulation
Our Application
Make It Right’s homes are built with materials that have higher R-Values than most standard homes. This higher R-value reduces air infiltration, increases the energy efficiency of our homes. Our R-Values are as follows:
- OSB SIP Walls (4.5”): R-17, 6.5”/R-25
- OSB SIP Roof (8.25”): R-33
- Sub-Floor Insulation: R-13